Master in Interior Design
Become an interior designer professional able to respond to the changes and needs of a society in constant evolution. Transform spaces, create experiences.
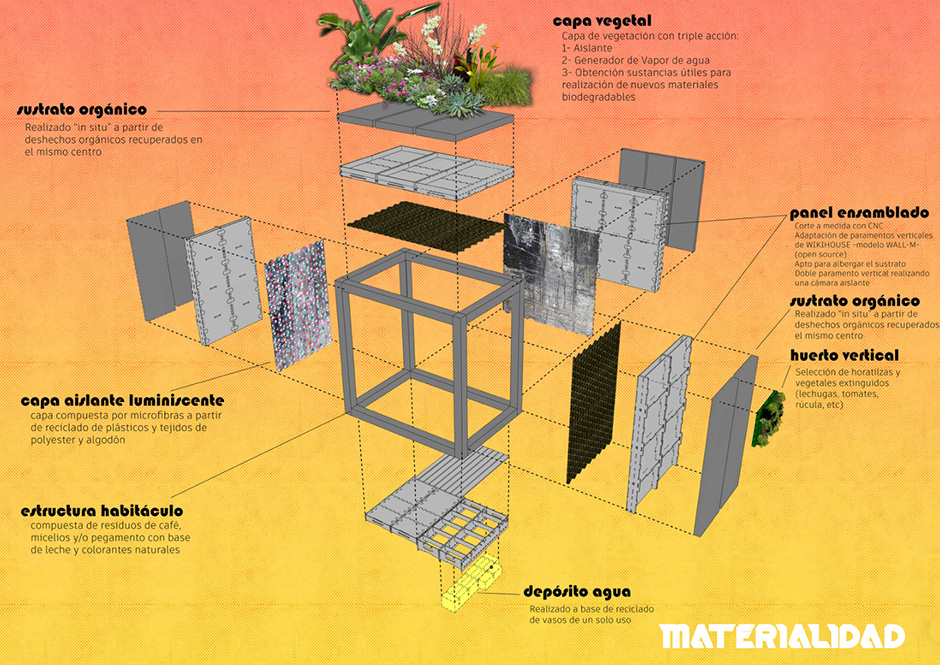
Description of the curriculum
- Edition: 4th
- Teaching period: from October 2024 to June 2025. Final master's project presentation: June 2025
- Schedule: Monday to Thursday from 4 p.m. to 7 p.m.
- Modality: on-site
- Language: Spanish
- Price: 9.320 €
- Qualification: Master's Degree in Interior Design awarded by the UVic-UCC
- Credits: 60
Presentation
The Master's Degree in Interior Design offers the tools and knowledge to explore all the creative possibilities of interior design. Through a holistic and transversal training with references to architecture, design and visual communication, among other disciplines, this course seeks to overcome the great challenges of the present with a critical spirit, imagination and sensitivity.
The master's programme studies and develops the key areas of interior design, from living spaces (domestic, academic, work) and leisure spaces (cultural, gastronomic) to public spaces in all their diversity. It explores homes, schools and offices as well as museums, restaurants and ephemeral constructions, focusing on tradition but also on innovation and disruption.
The master's degree considers interior spaces as a complete sensory experience that joins and combines matter, light, texture and colour, but also emotions, learning and coexistence, convinced of their fundamental role in a dynamic, constantly evolving society that requires a profound transformation of living spaces.
Open to design graduates and artists as well as engineers and architects, and with a global and plural approach, this course focuses on the students at all times, making them the active protagonists of an exciting research based on the pillars of contemporary design: creativity, sustainability, cooperation, health and wellbeing.
Syllabus
Module 1 - Projects Module 2 - Workshops on space Module 3 - Materiality and conditioning Module 4 - Representation Module 5 - Communication Module 6 - Master's final project
Programme
Module 1: Projects
The project as a key tool in professional design practice.
During this Master's course, a total of four projects will be completed, three of them in this module. In addition, this course will deal with project methodology as a tool (project intentions and strategies), the transfer of formal and conceptual references to project practice (imaginaries), and historical practice (history and culture of interior design applied to the realisation of current projects).
During project development, students will incorporate all the contents and tools that will be used simultaneously in the other modules.
The development of projects is hybridised with visits to designers’/architects' studios and visits to relevant centres/institutions. It is also complemented by the possibility of participating in competitions with a consolidated trajectory.
- (PI) Projects and spaces of privacy: homes, hotels, health and care spaces.
- (PII) Projects and spaces of interaction: work spaces, exhibition spaces, educational spaces, public spaces, cultural spaces, ephemeral architecture.
- (PIII) Projects and spaces of exchange: commercial spaces, gastronomic spaces, leisure spaces.
Students will also be able to propose projects for current hybrid spaces: home-workshops, home-offices, education-culture, etc.
Module 2: Space workshops
The workshop as a key methodology for exploration and the acquisition of knowledge through practice: learning by doing.
In the workshops that will take place in this module, students will carry out activities and practical exercises of short and medium duration with the aim of acquiring knowledge and incorporating it into the various projects that they will carry out simultaneously.
Space is inhabited: it transmits sensations, emotions, and is the container and wellspring of experiences. Exploring, knowing and harmonising materials, proportions, scales, light or people's movement, among others, are determining factors in the production of people-friendly spaces.
- Identification and representation of non-tangible attributes and tangible dimensions of space
- Perception: light and illumination, colour, sound, texture, movement. The inhabitant in space
- Atmospheres: material and sensory coherence and harmonisation
- Space and experience: emotional design, user-experience
- Space and time: flexibility, adaptability, evolving spaces
- Sustainability (social): empathy maps, co-design, relational design
- Space, context, and culture (place)
Module 3: Materiality and conditioning
Matter, technologies and energy as basic components of space.
Spatial design is a discipline that works with knowledge, materialities and technologies which are specific to it and which differ from place to place (material culture). Exploring them, getting to know them and mastering them is key to the realisation of design projects.
This module is completed with visits to works in progress by active professionals and makers of recognised interest (designers, artists, craftsmen and women).
Construction processes, spatial elements (walls and partitions, flooring, cladding, carpentry), and installations (sanitation, electricity, plumbing, gas, air conditioning).
- Space and objects: furniture design, product and space design, elements (sanitary ware, taps, kitchens...).
- From the project to the building site: regulations, technical documentation, measurements and budgets, planning and management of the work.
- Bio-construction, healthy spaces (comfort and well-being) and sustainability (energy and space, ecological footprint, recycling, reuse).
- Introduction to restoration and rehabilitation
- Material innovation
Module 4: Representation
Graphic expression as a fundamental tool in the process of a project and communication of spatial design.
In this module, different languages, tools and techniques for the representation of space will be explored and applied with the aim of enabling students to master different means for the development of design practices by discovering, establishing, designing and communicating through expressive processes.
- Two-dimensional graphic representation (drawing, CAD, Autocad), and three-dimensional (virtual models, renderings, 3ds Max)
- Models: strategies, materials and techniques for the elaboration of communicative and conceptual models
- Conceptual graphic representation: image post-processing (Photoshop) and atmospheric Moodboard
- The diagram as a graphic tool for projects and communication (Miro)
- Introduction to advanced graphic representation: BIM (Revit)
Module 5: Communication
In the current context, mastering graphic and audiovisual communication tools is key to any design practice.
In this module, communication projects will be designed and carried out within the framework of spatial design, applying appropriate, coherent and innovative tools and technologies.
- Elaboration and communication of project narratives
- Dialogue with the client and/or inhabitant: communicative strategies and techniques
- Audiovisual media as a tool for the communication of spatial design proposals
- Platforms and websites
- Interactive media and mapping as a communication tool
Module 6: Master's Final Project
The Master's Final Project is a tool for synthesising everything studied during the Master's course, and is also a vehicle for exploring and determining the personal identity necessary for developing professional practice.
In the Master's final project, a project oriented towards professional practice will be developed. Students will decide on the programme of uses (living spaces, cultural and leisure spaces, etc.) for which they wish to develop their proposal, including those aspects related to innovation dealt with in the master's degree.
Projects

Surf House: Un oasis moderno para teletrabajadores by Aleksandra Szczęch

Una a una. Centro ginecológico integral y holístico. by Ivanna Castillo

Hibridación de los Espacios a través de la Interacción by Camila Balbi
Teachers
Coordinator
Joan Maroto
Architect Doctor. Specialized in relational design and digital manufacturing
Pau Pericas
Master's Degree in Cinema and Audiovisual contemporary studies
Edurne Sanz
Architect and graphic designer. Specialized in Communication
Alba Méndez
Architect specialized in Neuroarchitecture
Queralt Garriga
Architecture, museography, heritage
David Batignani
Set designer, actor
Albert Cardellà
Architect and Landscaper. Specialized in design and innovation in sustainable public space
Yumi Martí
3D Artist. Interior designer
Nelson Jara
Actor. Theater director
Giovanna Pezzullo
Actress. Playwright. Sensory language teacher. Smell designer
Francisco Javier García
Teacher. Cultural Projects. Lighting Designer
Lisa Marrani
Doctora en Tecnología. Arquitecta
Kike Macías
Interior Designer
Silvia Bernad
Grau en Disseny / Postgrau en espais expositius / Màster oficial en recerca en art i disseny
Elisenda Rosàs
Architect specializing in restoration of architectural heritage
Career opportunities
- Designer specialist in interior spaces
- Collaborating designer in design and architecture studios
- Technical specialist in projects and management of interiors and space design works in companies in the sector
- Designer of ephemeral spaces (exhibitions, ephemeral architectures)
- Art direction in architecture and design
Within the BAU Design College framework, the master's degree offers professional connections with companies and/or design and architectural studios of renowned prestige with which students will be able to develop their professional career.
Payment methods
Total cost of the course: 9.320 €
The total cost includes an amount of 200 € concerning the university fees, the administration expenses and the compulsory insurances.
Payment methods
BAU, Arts and Design College of Barcelona offers different terms of payment:
-
Single payment
- Part payment, in 3 instalments:
- 1st payment, due on enrolment: consisting of 40 % of the fees excluding taxes. An amount of 200 € concerning the university fees is added to the resulting cost
- 2nd payment, due November 5: consisting of 30% of the course excluding taxes
- 3rd payment, due January 5: consisting of 30 % of the course excluding taxes
Students and former students of BAU benefit from 10% discount on any of the courses if they have exceeded at least 50% of the credits for a Degree, Higher Degree in Design or the Diploma in Graphic Design; or 100% of the credits for any of the Master’s or Postgraduate degrees.
More information about scholarships and grants.
Information about the registration process.
Academic regulations for Masters and Postgraduate Degrees of BAU.
Download the brochure
Enter your details and we will send you an email with the Master in Interior Design brochure.